Session 4 is about the applications used on a network both locally and remotely. The practical activity at the end of the session will look at how to set up remote access to a local area network using a VPN.
Topics
(Virtual Private Networking) VPN Explained
When a user accesses a website on the Internet, they start by connecting to a internet service provider (ISP). They are then redirected to any websites that they wish to visit. All the user’s internet traffic passes through the ISP’s servers, meaning the ISP can see and log everything the user is doing online. The ISP could hand the user’s browsing history over to advertisers, government agencies, and other interested oganisations.
To avoid this situation a VPN redirects the internet traffic through a specially configured remote server. This way, the VPN hides the IP address and encrypts all the data the user sends or receive. The encrypted data looks scrambled to anyone who intercepts it and it is impossible to read.
How does a VPN work?
When a VPN is turned on, your web traffic goes through a client that has been installed on your device. The client encrypts the traffic through one of several different protocols, generally either IPsec, PPTP or SSL/TLS. OpenVPN over SSL/TLS is considered the most secure option for normal use. The other protocols are older and may be vulnerable to state agencies.
The encrypted traffic then travels through your ISP’s servers, which means that your ISP can only see that you are using a VPN. They can no longer see exactly what you are doing. The traffic goes to the VPN server where it is decrypted before it heads off to its destination.
How Do I Use a VPN?
Using a VPN is a relatively straightforward process. For basic security and privacy needs, you don’t need to be a technological genius. The first step is to choose a VPN that you think will be suitable for your uses.
Once you have decided which one is right for you, you will need to subscribe to the service and download their client. Your provider’s website will have information on how to set it up. Once you have installed it, open up the client and make sure that it is configured appropriately for your usage. Once it is set up, all you have to do is turn it on and you are ready to browse safely and securely.
Things to consider when you are choosing a commercial VPN provider:
- Figure out what you need a VPN to doc.If you want a VPN for your entire network, a router-based VPN that allows for multiple simultaneous connections is what you should look for.If you’re planning on streaming movies online, you need a VPN with high speed, reliable connections, and unlimited bandwidth.
- Look at each VPN providers qualities.Every VPN company prioritizes something. It could be speed, it could be encryption, it could be anonymity – you need to make sure your priorities match theirs.If you want to watch content that is geographically blocked, a VPN that has a reputation to unlock content is a priority. For example man VPNs have trouble bypassing Netfilx geo block .If you are a person else who values their privacy and anonymity, a VPN that does not retain logs and has a secure encryption, should be your priority.
- Check which devices are compatible Although most VPNs support the main platforms of Windows, Mac, Linux, Android and iOS, some VPNs are not available on all platforms.I Some VPNs allow unlimited devices, while others only let you connect up to three.
- Find a VPN with a user-friendly interfaceThe setup and user-interface on a lot of VPNs can be quite complex. So, if you’re not tech savvy and do not want to trouble yourself trying to configure a VPN, it’s important to find one that offers simple procedures and a user-friendly platform.
- Ensure your important locations are covered The number of servers and locations can be the deciding factor for some VPNs.
VPN considerations for networks
One of the main disadvantages of using a VPN is that they will slow down the network connection. This is because it takes extra bandwidth to encrypt VPN traffic. This may not be a huge problem if you have a fast connection, but for any good network design these considerations should be understood and planned for before implementation.
Video Streaming – Broadband Speed And Bandwidth Requirements
The increasing popularity of streaming movies and TV shows over the Internet has brought with it some issues for many networks.
Some network wireless routers simply cannot cope with the speed needed to watch video without it being low quality and/or constantly buffering. This is evident when multiple sessions are open at the same time. This is why a well designed network with extra capacity is important.
For general information, below are the internet connection speed recommendations in Megabits per second (Mbps) per stream for playing movies and TV shows through various popular streaming services:
Netflix speed requirements per session
- 0.5 Mbps – minimum required connection speed
- 1.5 Mbps – minimum recommended speed
- 3.0 Mbps – recommended for SD quality
- 5.0 Mbps – recommended for HD quality
- 25 Mbps – recommended for Ultra HD quality
Bandwidth/data consumption.
Using Netflix as an example, watching movies or TV shows through that service requires about 1 GB of data per hour for each standard definition video stream and up to 3 GB per hour for each high definition video stream
As most providers have unlimited data plans today the main issue from the network design perspective will be the Quality of Service (QoS) given to the application.
As video demands tend to increase the traffic on the network increases so the QoS and segmentation is important.
Remote Access for a network.
Part of the planning for any good network design is how the remote access will be set up. The ability to gain access to network resources remotely is especially important for security and administration.
Today all vendors provide the ability to remotely access networks via the Internet. To ensure proper security is applied when using remote access a properly configured VPN client and server is required. The following practical activity is an example of how to remotely access a small network
Practical Activity
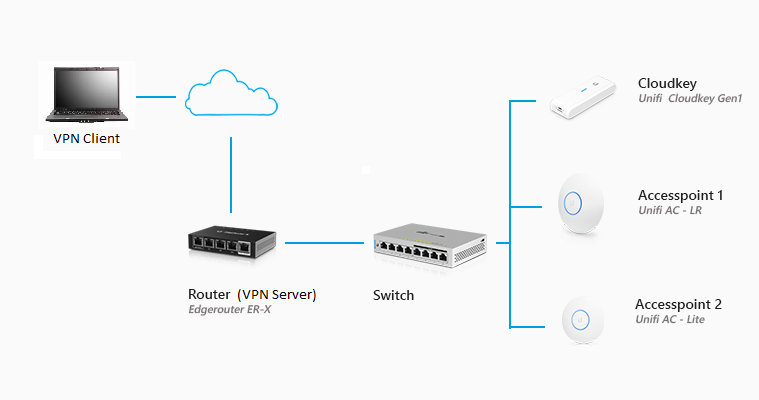
Using the above network diagram configure a Windows 10 VPN client for remote access to the VPN server
Windows 10 built in VPN client setup procedure.
Settings > Network & Internet > VPN > Add a VPN connection
- Windows VPN client settings
VPN Provider: Windows (built-in) Connection name: L2TP Server name: Router VPN Server VPN Type: L2TP/IPsec with pre-shared key Pre-shared key: <secret> Type of sign-in info: User name and password User name: <username> Password: <secret>
2. Navigate to the Windows 10 Network connections.
Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Change Adapter Options > L2TP Adapter properties
Security > Allow these protocols > Microsoft CHAP Version 2 (MS-CHAP v2)
3. Using the configured VPN client now connect to the VPN server on the router.
4. Open a web browser and and connect to the network Cloud key with https:// 192.168.1.1: 8443 If the VPN is working correctly you should see the following Unifi Controller screen.
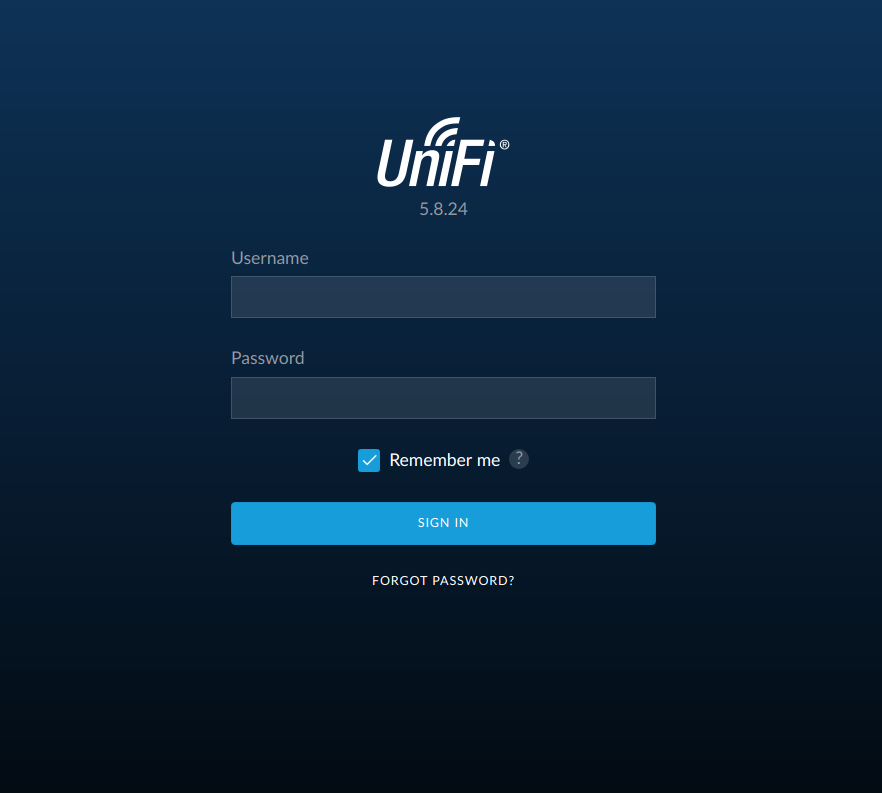
5. Login in to the controller with the admin account provided and navigate through the dashboard as directed.