Session 1 is designed to give an overview of how computer networks function . It covers the different types of connections available connecting to the Internet. It covers the different types of National Broadband Network (NBN) connections available as well as reference to the Sunshine Coast International Broadband Network.
This session is primarily designed to be delivered in a theory base format with interaction by the audience as required.
Topics covered:
Network concepts
What is a computer network.
- Local Area Network (LAN),
- Wide Area Network (WAN).
- Local Storage
- Cloud Storage
Internet overview
The Internet is the global system of interconnected computer networks that use the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to link devices worldwide. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, telephony, and file sharing.
Sunshine Coast International Broadband Cable
The Sunshine Coast International Broadband Cable
NBN Infrastructure
Networks managed by individual Retail Service Providers (RSPs) connect to the main NBN infrastructure through points of interconnect (POIs). There are 121 POIs across Australia, housed inside Telstra-owned telephone exchanges. The POIs then connect to large domestic back haul carrier networks then out to international networks.
The NBN connections
NBN connection use Multi Technology Mix (MTM) consisting of the following network technologies:
Wired:
- Fibre to the building (FTTB) – Used for multi-dwelling units and apartment blocks. Equivalent to FTTN, with the “node” located inside the building’s communications room. Also known as fibre to the basement.
- Fibre to the curb (FTTC) – Previously called fibre to the distribution point (FTTdp). Fibre connection to a communications pit on the street, then copper to the premises. Replacing Optus HFC from 2017. Also known as fibre to the pit.
- Fibre to the node (FTTN) – A mix of copper and fibre optic technology, providing most NBN connections. Minimum speed of 25 Mbit/s.
- Fibre to the premises (FTTP) – Fibre optic connection using a gigabit passive optical network. Available for greenfield development.
- Hybrid fibre-coaxial (HFC) – Uses a mix of fibre optic and CATV technology largely built on Telstra’s HFC network
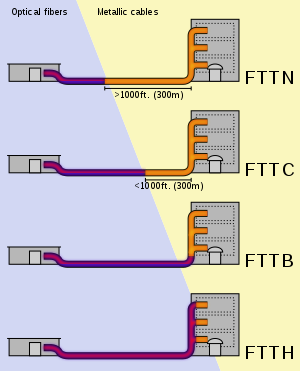
NBN Wired connection Comparison diagram
Wireless:
- Fixed wireless
- Satellite – Sky Muster telecommunications satellites
Refer to the NBN Connections page for further detail on the connection types
NBN Role
NBN Co is a data network wholesaler. NBN Co provides wholesale broadband to Retail Service Providers (RSPs) on a non-discriminatory basis . They provide the physical connection point into the customers premises.
RSP Role
Retail Service Providers such as Telstra, Optus TPG, Aussie Broadband and iinet connect the customers to the NBN access network for access to Internet.
Practical Activity
Using the NBN rollout map identify what type of NBN connection is available at your address.
- Determine the link speed requirements based on your needs for the NBN connection using this calculator.
- Use a web search engine to identify 3 suitable RSPs based on the results from the calculation
- Prepare a table comparing all the inclusions of the 3 providers internet plans.
Based on the information collected, list in order of ranking your choice of internet provider. Identify the pro and cons for your selection.