Session 6. This session outlines the techniques on how to secure and segment a network to accommodate the expanding need for smart software and hardware applications .
Topics
Smart Networks
With the introduction of so called smart devices such as energy monitors , climate controllers, media systems and voice assistants networks are growing in complexity .
It is common now for networks to have multiple devices connected to to an internet cloud based server communicating on a permanent basis. These networks accommodate many wireless connections constantly sending and receiving data.
In most systems the more demands that are placed on the resources the more the system will slow down and become less responsive. This is true for computer networks. Even home networks now can have more than 20 devices connected at any time. Game consoles , voice activation, media steaming devices and video surveillance are now standard applications.
The existing home or small business network probably has a single LAN segment connected to a multipurpose wireless router with an inbuilt 4 port switch. This type a setup is not able to cope with the demands of an growing network.
Smart Network Design
So with this in mind what is the process for planning a smart network for future expansion.
- Understand what applications are running on the network.
- Plan for additional applications based on user and business needs
- Look at the current infrastructure and identify the potential bottlenecks that could impact on performance.
- Document the network design to accommodate the expansion requirements.
- Build the network so it can be scalable for future needs.
1 Understand what applications are running on the network.
Existing small business and home networks probably started with a standard connection to the ISP. Typical Internet applications would have been web browsing, email, social media and VOIP. Local network applications could include office programs and printing.
The applications now have increased to include video streaming using wired and wireless connections. Applications and file sharing have become cloud based with more mobile devices connecting using Wi-Fi.
2. Plan for additional applications based on user and business needs
Providing permanent access to data and programs locally and remotely is becoming a necessity for networks. More vendors are using a cloud based model for applications. Video communication requiring large bandwidth has become standard. More devices are connecting using wireless to networks.
Smart monitoring devices working with Digital voice assistants are becoming common placing extra load on networks and introducing potential security issues.
With this in mind now we look at the current network structure.
3 Current infrastructure and identify the potential bottlenecks
The standard network connection provide by the ISP is the multipurpose wireless router shown below.

As mentioned previously these are the swiss army knife devices supplied at low cost designed to do routing, switching and wireless access. The diagram below shows a typical network constructed with a ISP supplied wireless router.
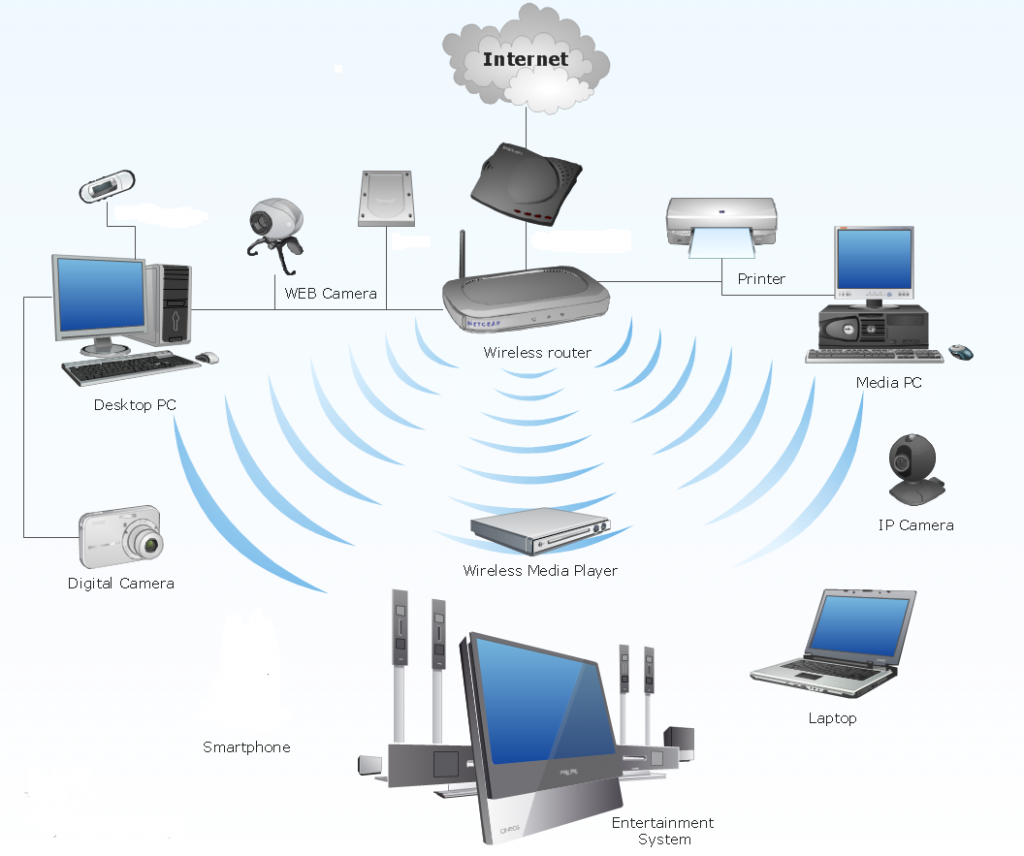
These wireless router devices are not expandable and suffer from the following:
- Limited to where they can be located on the premises. This may not be suitable for the best Wi-Fi connection.
- Small number of switch ports, typically four without any PoE capability
- Usually fairly basic firmware lacking advance functions such as VPN, segmentation and Quality of Service. (QoS)
- Suffer from performance issues when increased load is placed on router CPU.
- No ability to separate the IOT smart devices from the core network.
For these reasons it is best to redesign the network prior to expansion in this instance.
4.Document the network design to accommodate the expansion requirements.
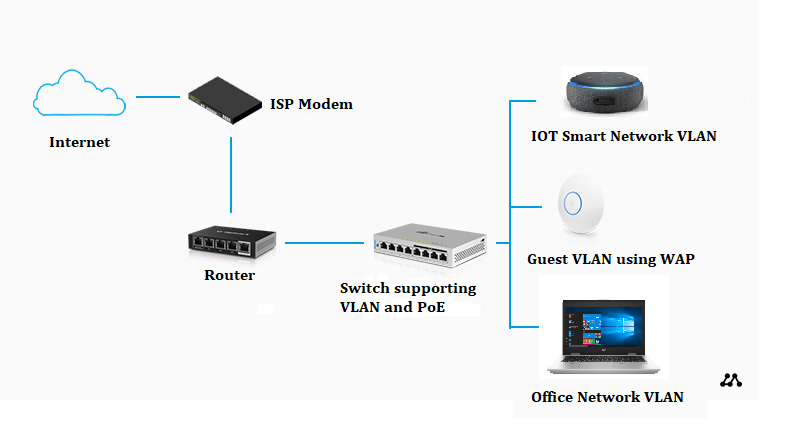
As the network expands the main thing to do is to structure the network into suitable managed segments. Typically this is done using Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) technology via dedicated hardware.
A well designed structured network should contain the following :
- Dedicated hardware to allow for expansion include:
- Router to handle WAN traffic with a VPN, QoS, Advanced Firewall
- Switches supporting VLANs , PoE and trunking
- Wireless Access Points (WAPs) providing sufficient coverage for network area.
- Proper Segmentation
- Main segment for normal business and office applications
- Guest segment to provide Internet access for visitors
- IOT segment to separate the smart devices into secure area.
- Firewall rules sets using the RFC 1918 IP address ranges for LAN access between segments.
- Sufficient capacity to allow for expansion for the 5 year period.
The diagram below outlines a typical structured network based on the requirements mentioned.
Practical activity.
Part 1.
Using the structured network diagram as a guide design a smart network with the following requirements:
- Main network to support 10 users. Applications used are Office 365, social media and accounting software. Users access network via wired and wireless connections.
- Guest network to allow authorized visitors to access the Internet.
- Smart network to support digital assistant, energy monitoring devices and media streaming.
- Support for network video recording using PoE connections.
- Use RFC 1918 for private IP addressing
Part 2
Build and test your design incorporating the following firewall rules.
- Main network to have access to all VLANs
- Guest network to have access to Internet during business hours only
- Remote access via VPN for management .